Recovery Self Care
When you have a VAD there is a lot for you and your caregivers to learn.
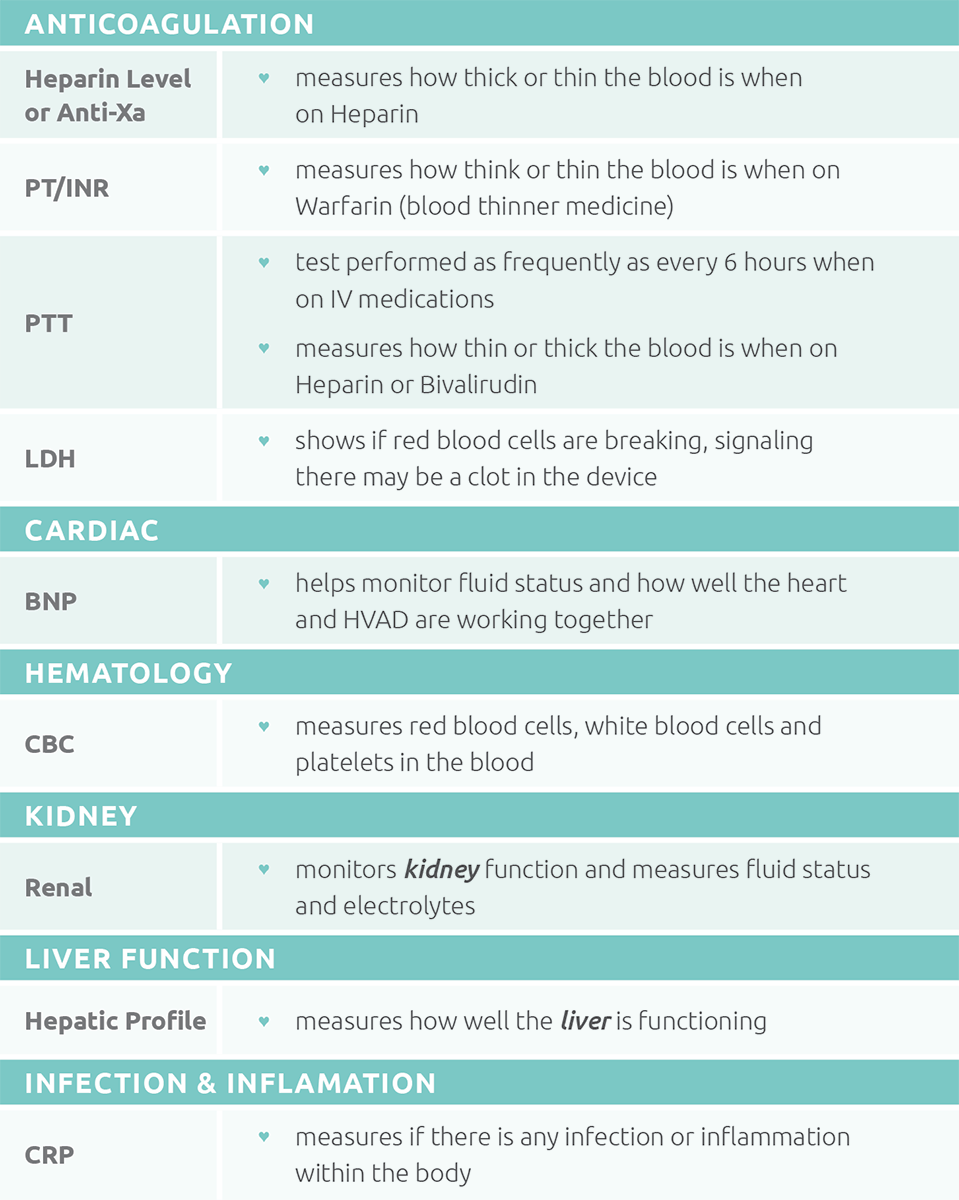
What labs could you need?
You will have laboratory testing (labs or bloodwork) done at various scheduled times or whenever your care team feels they need to follow you closer. These labs tell your care team how well your body is functioning with the new device.
Click on the image to view a list of possible requested labs.
What tests could you need?
Testing will become part of normal life. Testing will be done at scheduled times and whenever your team feels like you may need closer surveillance.
- IMPORTANT: Once you have a VAD, DO NOT have an MRI test. An MRI uses strong magnets that attract metal objects and would damage your VAD.
Common tests include:
- CT Scan: If the VAD is acting unusual or your LDH is high, your team may order a CT scan of your heart to check for a clot in the device. A CT of your head may be done if there is a concern for stroke.
- Echocardiogram: An “Echo” is an ultrasound that uses nonradioactive, high-frequency sound waves to view your heart. An Echo is a non-invasive test and helps the care team to diagnose any heart or VAD problems.
- Exercise Testing: To determine how well you are doing on the VAD, your team may order an exercise test. The exercise test may be done on a stationary bike, a treadmill, or they may have you do a 6 minute walk.
- Ramp Study: A Ramp Study is done to determine the best RPM setting for you. The team will watch how your heart looks as they change the speed of the device.
What medicines could you take?
In the hospital, medicine will be given through an IV. Your care team will change those medicines to be given by mouth when preparing for discharge. It’s important the medicines are taken at the same time every day. By the time you are ready to go home, medicines will likely be taken twice a day. Use a pill box to keep your medicines organized. Inform your care team if you take any additional medicines NOT prescribed by them. Learn more about medicines through the interactive below.
Blood Thinning Medicines
When you are on a VAD, you will always be on blood thinner (anticoagulation) medicines. Your care team will increase and decrease the medicines based on your lab results.
Aspirin
You will take aspirin to prevent platelets from sticking together and forming a clot in your VAD.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Warfarin is the most important medicine you will take, but it can be difficult to get your dose (the amount you take) correct. The dose needed will go up and down frequently depending on your INR. Warfarin is what makes your INR (blood levels for anticoagulation or how thick or thin your blood is) increase. In can be tricky because it interacts with lots of different medicines and foods. Your INR can change dramatically with your diet. Warfarin blocks the ability for the body to activate Vitamin K, which helps your body produce blood clots. Green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin K. Eating lots of these types of foods can decrease your INR or make your blood thicker. It is important to have a consistent diet that includes serving of foods that contain similar amounts of vitamin K each week.

Causes for High INR (thin blood):
- New medicines
- Prolonged vomiting/diarrhea*
- Prolonged inability to eat*
- An increase in alcohol consumption
- A decreased intake of food or drink containing vitamin K
Causes for Low INR (thick blood):
- Missed doses of warfarin
- An increased intake of food or drink containing vitamin K
- Large increase in exercise
Learn more about warfarin (Coumadin) in the Exploring Medicine Treatment Options module and learn more about anticoagulation through the interactive below.
High Blood Pressure Medicines
At times, with a VAD you may have high blood pressure and require medicines to keep the VAD pumping well and can decrease your risk of stroke.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are given in the operating room and ICU to prevent infection. They are also given if your driveline gets infected. Antibiotics can make your INR high or low. Immediately notify your care team if you start taking an antibiotic.
Stomach Ulcer & Acid Reflux Medicines
Medicines to prevent “heartburn” are used to decrease the acid in the stomach. This may help with decreasing any stomach discomfort you may have.
Diuretics (medicines to remove extra body water)
Diuretics were important when you were in heart failure. When you are on a VAD you should need less, but you still may need a small amount to get the fluids in your body just right.
What complications could occur?
Most of the following complications are rare and your care team will be with there to help keep you safe.
Bleeding
When on blood thinners, you are always at risk of bleeding. You may experience bleeding from your gums when brushing your teeth and your cuts may bleed more than normal. Girls may experience heavier bleeding during menstrual periods and may need to seek additional treatment. If you are involved in a traumatic accident, such as a car accident, it can be harder to stop the bleeding.
Nose Bleeds
To prevent nose bleeds, use petroleum jelly or saline nose spray in your nasal passages during cold, dry weather. Do not pick your nose as this may start a nosebleed. If you have a nose bleed:
- Stay calm. Look forward. Do not tilt your head back.
- Hold pressure at the bridge of your nose for 10 minutes without letting go.
- If pressure doesn’t stop the bleeding, your care team may advise you to use Afrin® or saline nasal spray.
- Let your care team know if you can’t stop the bleeding, or if you have frequent nose bleeds.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeds
Learn more about the risks and signs of bleeding in your belly in the interactive below.
Stroke
With all VADs there is a risk of stroke, which is caused by bleeding or a blood clot in your brain. Both may cause injury to your brain. Your care team manages your medicines carefully to prevent strokes, however sometimes strokes may occur. Notify your care team or call 911 if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Headaches that are different than usual
- Numbness and/or tingling on one side of the body
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Losing feeling and/or movement in the legs or arms
- Slurring words or trouble when talking
- Facial expressions and movements don’t match (or mirror) on each side of the face
- Pupil (the dark circle in the middle of the eye) sizes don’t match

Download PDF
Hemolysis
Red blood cells help carry oxygen to your tissues and organs. When red blood cells get broken down, this is called hemolysis. Hemolysis may occur for multiple reasons, the most concerning being a mechanical problem with the VAD. Notify your care team if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Pink, red, cola, or tea colored urine
- Increased pump power/flow that is out of your range
- Decreased pump power that is out of your range
Learn more about what to look out for in the interactive below:
Pump Clots
Rarely will the VAD develop a clot inside of it and not work properly. If this happens, and changes to your blood thinner medicine doesn’t fix the problem, you may need to get a new VAD.
What should you know about your blood pressure?
Keeping your blood pressure in a healthy range is very important. Your care team will determine a target blood pressure goal and adjust medicines to meet it. Blood pressure can be monitored using a blood pressure cuff and/ or a Doppler. This depends on if you can feel a pulse. If you go to an outside hospital you may need to tell them the best way to take your blood pressure.
Learn more in the interactive below about how your care team will help you stay at a healthy blood pressure.
How do you care for your driveline site?
Caring for your driveline will help you avoid getting an infection. Germs that collect at the driveline site could travel to the heart if left untreated. Frequent movement of the driveline can cause damage above and underneath the skin and increase the risk of infection. Using anchors to keep the driveline in place is important to keep the driveline site healthy.
If you notice any changes in your driveline or if your driveline gets pulled, tell your care team right away so it can be treated quickly. Signs and symptoms of a driveline infection include:
- Redness
- Pain or tenderness
- Drainage (new or increased)
- Swelling and warmth
Learn more about what to look out for through the infection interactive below
Dressing Changes
Your driveline site will need to have dressing changes using a sterile technique. Everyone should use sterile gloves and wear masks during dressing changes. How often you change your dressings will be determined by your care team.
Learn more about how to properly clean and take care of your driveline in the interactive below.
What should you be eating and drinking?
Once you have your VAD, you must stay on a stable diet. Eating a consistent healthy diet will help you heal and get stronger.
Fluid balance is very important to maintain VAD flow. Dehydration from not drinking enough or increased fluid losses (vomiting, diarrhea, sweating) will lead to low VAD blood flow.
- lightheadedness, tiredness, falls
- alarms from your VAD
- swollen face, hands or legs
- poor appetite
- shortness of breath

How are you feeling?
For some patients, having a VAD and needing lots of medical care can be hard. Many patients that have VAD surgery notice an improvement in symptoms while they are in the hospital, but it can take months for you to get stronger and recover. As you recover, you or your caregiver may feel sad, worried, or even angry at times. This is normal. Be honest about how you’re feeling and talk with your care team if you have these feelings or any changes in behavior. Taking care of your emotional and mental health is a very important part of your care. Your care team will be able to connect you with the right support services.